Page 16 - EASL Recommendations on Treatment of Hepatitis C 2015 - Summary
P. 16
17. Tables
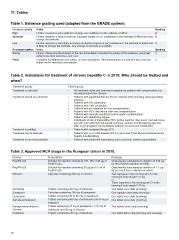
Table 1. Evidence grading used (adapted from the GRADE system).
Evidence quality Notes Grading
High A
Moderate Further research is very unlikely to change our confidence in the estimate of effect B
Low Further research is likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and may C
change the estimate
Recommendation Grading
Strong Further research is very likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and 1
is likely to change the estimate. Any change of estimate is uncertain
Weak 2
Notes
Factors influencing the strength of the recommendation included the quality of the evidence, presumed
patient-important outcomes, and cost
Variability in preferences and values, or more uncertainty. Recommendation is made with less certainty,
higher cost or resource consumption
Table 2. Indications for treatment of chronic hepatitis C in 2015: Who should be treated and
when?
Treatment priority Patient group
Treatment is indicated
Treatment should be prioritized • All treatment-naïve and treatment-experienced patients with compensated and
decompensated liver disease
Treatment is justified
Treatment can be deferred • Patients with significant fibrosis (F3) or cirrhosis (F4), including decompensated
Treatment is not recommended cirrhosis
• Patients with HIV coinfection
• Patients with HBV coinfection
• Patients with an indication for liver transplantation
• Patients with HCV recurrence after liver transplantation
• Patients with clinically significant extra-hepatic manifestations
• Patients with debilitating fatigue
• Individuals at risk of transmitting HCV (active injection drug users, men who have
sex with men with high-risk sexual practices, women of child-bearing age who
wish to get pregnant, haemodialysis patients, incarcerated individuals)
• Patients with moderate fibrosis (F2)
• Patients with no or mild disease (F0-F1) and none of the above-mentioned extra-
hepatic manifestations
• Patients with limited life expectancy due to non-liver related comorbidities
Table 3. Approved HCV drugs in the European Union in 2015.
Product Presentation Posology
PegIFN-α2a Solution for injection containing 180, 135 or 90 µg of Once weekly subcutaneous injection of 180 µg
PegIFN-α2a (or less if dose reduction needed)
PegIFN-α2b Solution for injection containing 50 µg per 0.5 ml of Once weekly subcutaneous injection of 1.5 µg/
PegIFN-α2b kg (or less if dose reduction needed)
Ribavirin Capsules containing 200 mg of ribavirin Two capsules in the morning and 3 in the
evening if body weight <75 kg
Sofosbuvir Tablets containing 400 mg of sofosbuvir or
Simeprevir Capsules containing 150 mg of simeprevir Three capsules in the morning and 3 in the
Daclatasvir Tablets containing 30 or 60 mg of daclatasvir evening if body weight ≥75 kg
Sofosbuvir/ledipasvir Tablets containing 400 mg of sofosbuvir and 90 mg of One tablet once daily (morning)
ledipasvir One capsule once daily (morning)
Paritaprevir/ombitasvir/ Tablets containing 75 mg of paritaprevir, 12.5 mg of One tablet once daily (morning)
ritonavir ombitasvir and 50 mg of ritonavir One tablet once daily (morning)
Dasabuvir Tablets containing 250 mg of dasabuvir
Two tablets once daily (morning)
One tablet twice daily (morning and evening)
15
Table 1. Evidence grading used (adapted from the GRADE system).
Evidence quality Notes Grading
High A
Moderate Further research is very unlikely to change our confidence in the estimate of effect B
Low Further research is likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and may C
change the estimate
Recommendation Grading
Strong Further research is very likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and 1
is likely to change the estimate. Any change of estimate is uncertain
Weak 2
Notes
Factors influencing the strength of the recommendation included the quality of the evidence, presumed
patient-important outcomes, and cost
Variability in preferences and values, or more uncertainty. Recommendation is made with less certainty,
higher cost or resource consumption
Table 2. Indications for treatment of chronic hepatitis C in 2015: Who should be treated and
when?
Treatment priority Patient group
Treatment is indicated
Treatment should be prioritized • All treatment-naïve and treatment-experienced patients with compensated and
decompensated liver disease
Treatment is justified
Treatment can be deferred • Patients with significant fibrosis (F3) or cirrhosis (F4), including decompensated
Treatment is not recommended cirrhosis
• Patients with HIV coinfection
• Patients with HBV coinfection
• Patients with an indication for liver transplantation
• Patients with HCV recurrence after liver transplantation
• Patients with clinically significant extra-hepatic manifestations
• Patients with debilitating fatigue
• Individuals at risk of transmitting HCV (active injection drug users, men who have
sex with men with high-risk sexual practices, women of child-bearing age who
wish to get pregnant, haemodialysis patients, incarcerated individuals)
• Patients with moderate fibrosis (F2)
• Patients with no or mild disease (F0-F1) and none of the above-mentioned extra-
hepatic manifestations
• Patients with limited life expectancy due to non-liver related comorbidities
Table 3. Approved HCV drugs in the European Union in 2015.
Product Presentation Posology
PegIFN-α2a Solution for injection containing 180, 135 or 90 µg of Once weekly subcutaneous injection of 180 µg
PegIFN-α2a (or less if dose reduction needed)
PegIFN-α2b Solution for injection containing 50 µg per 0.5 ml of Once weekly subcutaneous injection of 1.5 µg/
PegIFN-α2b kg (or less if dose reduction needed)
Ribavirin Capsules containing 200 mg of ribavirin Two capsules in the morning and 3 in the
evening if body weight <75 kg
Sofosbuvir Tablets containing 400 mg of sofosbuvir or
Simeprevir Capsules containing 150 mg of simeprevir Three capsules in the morning and 3 in the
Daclatasvir Tablets containing 30 or 60 mg of daclatasvir evening if body weight ≥75 kg
Sofosbuvir/ledipasvir Tablets containing 400 mg of sofosbuvir and 90 mg of One tablet once daily (morning)
ledipasvir One capsule once daily (morning)
Paritaprevir/ombitasvir/ Tablets containing 75 mg of paritaprevir, 12.5 mg of One tablet once daily (morning)
ritonavir ombitasvir and 50 mg of ritonavir One tablet once daily (morning)
Dasabuvir Tablets containing 250 mg of dasabuvir
Two tablets once daily (morning)
One tablet twice daily (morning and evening)
15