Page 9 - EASL Recommendations on Treatment of Hepatitis C 2015 - Full version
P. 9
Clinical Practice Guidelines
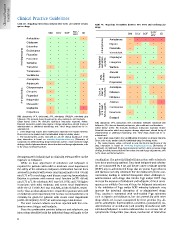
Table 4D. Drug-drug interactions between HCV DAAs and central nervous Table 4E. Drug-drug interactions between HCV DAAs and cardiovascular
system drugs. drugs.
SIM DCV SOF SOF/ 3D SIM DCV SOF SOF/ 3D
LDV LDV
•
Amitriptyline ••• •• Antiplatelet Amiodarone ••• • •
Citalopram and antico- Antiarrythmics Digoxin •
Duloxetine ••• •• Flecainide ••• • •
Escitalopram agulants Vernakalant •
Fluoxetine ••• •• Clopidogrel ••• •
Paroxetine
Anti-depressants Sertraline ••• •• ••• •
Trazodone
Trimipramine ••• ••
Venlafaxine
Amisulpiride ••• •• ••• •
Aripiprazole
Chlorpromazine ••• •• Dabigatran ••• • •
Clozapine Warfarin ••• • •
Flupentixol ••• •• Atenolol ••• • •
Haloperidol Bisoprolol ••• • •
Olanzapine ••• •• Propranolol ••• • •
Quetiapine Amlodipine ••• • •
Risperidone ••• •• Beta
blockers
••• ••
••• ••
Anti-psychotics ••• •• Calcium
channel
••• •• blockers Diltiazem ••• • •
Nifedipine ••• • •
••• •• Aliskiren ••• • •
••• ••
••• •• Hypertension
and heart
••• •• Candesartan • •• • •
failure agents
••• •• Doxazosin ••• • •
SIM, simeprevir; DCV, daclatasvir; SOF, sofosbuvir; SOF/LDV, sofosbuvir plus Enalapril ••• • •
ledipasvir; 3D, ritonavir-boosted paritaprevir, plus ombitasvir and dasabuvir.
Colour legend. Green: No clinically significant interaction expected. Amber: SIM, simeprevir; DCV, daclatasvir; SOF, sofosbuvir; SOF/LDV, sofosbuvir plus
Potential interaction which may require a dosage adjustment, altered timing of ledipasvir; 3D, ritonavir-boosted paritaprevir, plus ombitasvir and dasabuvir.
administration or additional monitoring. Red: These drugs should not be co- Colour legend. Green: No clinically significant interaction expected. Amber:
administered. Potential interaction which may require a dosage adjustment, altered timing of
Some drugs may require dose modifications dependent on hepatic function. administration or additional monitoring. Red: These drugs should not be co-
Please refer to the product label for individual drugs for dosing advice. administered.
The symbol (green, amber, red) used to rank the clinical significance of the Some drugs may require dose modifications dependent on hepatic function.
drug interaction is based on www.hep-druginteractions.org (University of Please refer to the product label for individual drugs for dosing advice.
Liverpool). For additional drug-drug interactions and for a more extensive range The symbol (green, amber, red) used to rank the clinical significance of the
of drugs, detailed pharmacokinetic interaction data and dosage adjustments, refer drug interaction is based on www.hep-druginteractions.org (University of
to the above-mentioned website. Liverpool). For additional drug-drug interactions and for a more extensive range
of drugs, detailed pharmacokinetic interaction data and dosage adjustments, refer
to the above-mentioned website.
decompensated cirrhosis) had no clinically relevant effect on the combination. The potential (limited) interactions with sofosbuvir
exposure to ledipasvir. have been previously outlined. Since both ledipasvir and sofosbu-
vir are transported by P-gp and breast cancer resistant protein
While no dose adjustment of sofosbuvir and ledipasvir is (BCRP), any co-administered drugs that are potent P-gp inducers
required for patients with mild or moderate renal impairment, will decrease not only sofosbuvir but also ledipasvir plasma con-
the safety of the sofosbuvir-ledipasvir combination has not been centrations, leading to reduced therapeutic effect. Although co-
assessed in patients with severe renal impairment (eGFR <30 ml/ administration with drugs that inhibit P-gp and/or BCRP may
min/1.73 m2) or end-stage renal disease requiring haemodialysis. increase the exposure of sofosbuvir and ledipasvir, clinical conse-
Relative to patients with normal renal function (eGFR >80 ml/ quences are unlikely. One area of focus for ledipasvir interactions
min/1.73 m2), the sofosbuvir AUC was 61%, 107%, and 171% higher is the inhibition of P-gp and/or BCRP whereby ledipasvir may
in patients with mild, moderate and severe renal impairment, increase the intestinal absorption of co-administered drugs.
while the GS-331007 AUC was 55%, 88%, and 451% higher, respec- Thus, caution is warranted with well-studied P-gp substrates
tively. Thus, no dose adjustment is required for patients with mild such as digoxin and dabigatran, but also potentially with other
or moderate renal impairment, but no dose recommendation can drugs which are, in part, transported by these proteins (e.g. ali-
currently be given for patients with severe renal impairment skrein, amlodipine, buprenorphine, carvedilol, cyclosporine). Co-
(eGFR <30 ml/min/1.73 m2) or with end-stage renal disease. administration of amiodarone (and possibly dronedarone) with
sofosbuvir/ledipasvir is contra-indicated due to a serious risk of
The most common adverse reactions reported with this com- symptomatic bradycardia (see above, mechanism of interaction
bination were fatigue and headache.
Since the combination contains ledipasvir and sofosbuvir, any
interactions identified with the individual drugs will apply to the
8
Table 4D. Drug-drug interactions between HCV DAAs and central nervous Table 4E. Drug-drug interactions between HCV DAAs and cardiovascular
system drugs. drugs.
SIM DCV SOF SOF/ 3D SIM DCV SOF SOF/ 3D
LDV LDV
•
Amitriptyline ••• •• Antiplatelet Amiodarone ••• • •
Citalopram and antico- Antiarrythmics Digoxin •
Duloxetine ••• •• Flecainide ••• • •
Escitalopram agulants Vernakalant •
Fluoxetine ••• •• Clopidogrel ••• •
Paroxetine
Anti-depressants Sertraline ••• •• ••• •
Trazodone
Trimipramine ••• ••
Venlafaxine
Amisulpiride ••• •• ••• •
Aripiprazole
Chlorpromazine ••• •• Dabigatran ••• • •
Clozapine Warfarin ••• • •
Flupentixol ••• •• Atenolol ••• • •
Haloperidol Bisoprolol ••• • •
Olanzapine ••• •• Propranolol ••• • •
Quetiapine Amlodipine ••• • •
Risperidone ••• •• Beta
blockers
••• ••
••• ••
Anti-psychotics ••• •• Calcium
channel
••• •• blockers Diltiazem ••• • •
Nifedipine ••• • •
••• •• Aliskiren ••• • •
••• ••
••• •• Hypertension
and heart
••• •• Candesartan • •• • •
failure agents
••• •• Doxazosin ••• • •
SIM, simeprevir; DCV, daclatasvir; SOF, sofosbuvir; SOF/LDV, sofosbuvir plus Enalapril ••• • •
ledipasvir; 3D, ritonavir-boosted paritaprevir, plus ombitasvir and dasabuvir.
Colour legend. Green: No clinically significant interaction expected. Amber: SIM, simeprevir; DCV, daclatasvir; SOF, sofosbuvir; SOF/LDV, sofosbuvir plus
Potential interaction which may require a dosage adjustment, altered timing of ledipasvir; 3D, ritonavir-boosted paritaprevir, plus ombitasvir and dasabuvir.
administration or additional monitoring. Red: These drugs should not be co- Colour legend. Green: No clinically significant interaction expected. Amber:
administered. Potential interaction which may require a dosage adjustment, altered timing of
Some drugs may require dose modifications dependent on hepatic function. administration or additional monitoring. Red: These drugs should not be co-
Please refer to the product label for individual drugs for dosing advice. administered.
The symbol (green, amber, red) used to rank the clinical significance of the Some drugs may require dose modifications dependent on hepatic function.
drug interaction is based on www.hep-druginteractions.org (University of Please refer to the product label for individual drugs for dosing advice.
Liverpool). For additional drug-drug interactions and for a more extensive range The symbol (green, amber, red) used to rank the clinical significance of the
of drugs, detailed pharmacokinetic interaction data and dosage adjustments, refer drug interaction is based on www.hep-druginteractions.org (University of
to the above-mentioned website. Liverpool). For additional drug-drug interactions and for a more extensive range
of drugs, detailed pharmacokinetic interaction data and dosage adjustments, refer
to the above-mentioned website.
decompensated cirrhosis) had no clinically relevant effect on the combination. The potential (limited) interactions with sofosbuvir
exposure to ledipasvir. have been previously outlined. Since both ledipasvir and sofosbu-
vir are transported by P-gp and breast cancer resistant protein
While no dose adjustment of sofosbuvir and ledipasvir is (BCRP), any co-administered drugs that are potent P-gp inducers
required for patients with mild or moderate renal impairment, will decrease not only sofosbuvir but also ledipasvir plasma con-
the safety of the sofosbuvir-ledipasvir combination has not been centrations, leading to reduced therapeutic effect. Although co-
assessed in patients with severe renal impairment (eGFR <30 ml/ administration with drugs that inhibit P-gp and/or BCRP may
min/1.73 m2) or end-stage renal disease requiring haemodialysis. increase the exposure of sofosbuvir and ledipasvir, clinical conse-
Relative to patients with normal renal function (eGFR >80 ml/ quences are unlikely. One area of focus for ledipasvir interactions
min/1.73 m2), the sofosbuvir AUC was 61%, 107%, and 171% higher is the inhibition of P-gp and/or BCRP whereby ledipasvir may
in patients with mild, moderate and severe renal impairment, increase the intestinal absorption of co-administered drugs.
while the GS-331007 AUC was 55%, 88%, and 451% higher, respec- Thus, caution is warranted with well-studied P-gp substrates
tively. Thus, no dose adjustment is required for patients with mild such as digoxin and dabigatran, but also potentially with other
or moderate renal impairment, but no dose recommendation can drugs which are, in part, transported by these proteins (e.g. ali-
currently be given for patients with severe renal impairment skrein, amlodipine, buprenorphine, carvedilol, cyclosporine). Co-
(eGFR <30 ml/min/1.73 m2) or with end-stage renal disease. administration of amiodarone (and possibly dronedarone) with
sofosbuvir/ledipasvir is contra-indicated due to a serious risk of
The most common adverse reactions reported with this com- symptomatic bradycardia (see above, mechanism of interaction
bination were fatigue and headache.
Since the combination contains ledipasvir and sofosbuvir, any
interactions identified with the individual drugs will apply to the
8